GIS Visualization
GIS is a visualization that displays the data in Geographical Information System. It uses data that is attached to a unique location. GIS is a computer-based tool used to store, visualize, and interpret geographic data that identifies the geographic location of features with the help of Latitude and Longitude data.
In the example below, GIS is created with “Latitude and Longitude” as columns, to analyse Global data.
To create a GIS
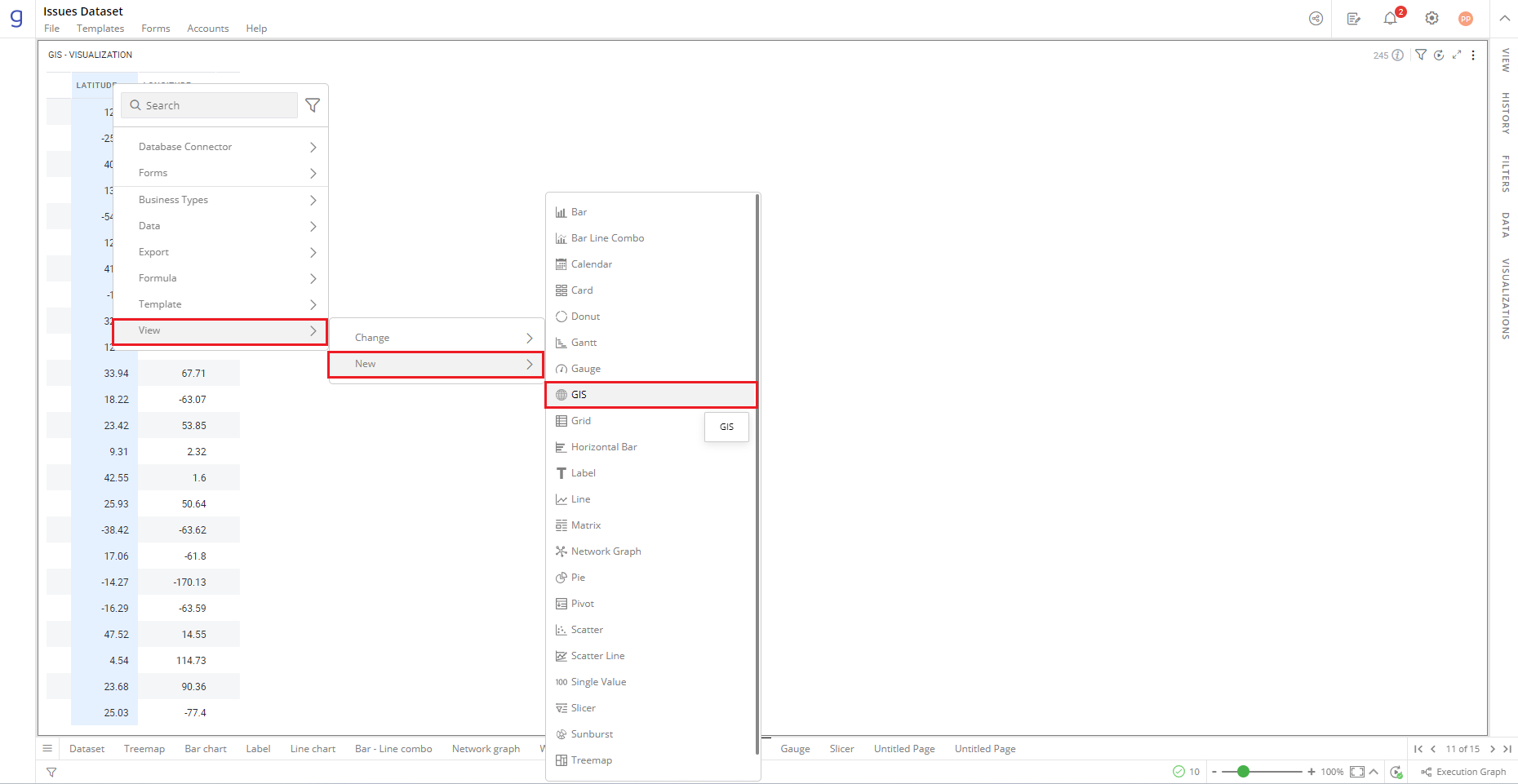
- Right-click on the ‘Component(s)’ column > Select View> Change>GIS.
Refer here to learn more about creating a visualization.
The following figure shows the resulting GIS: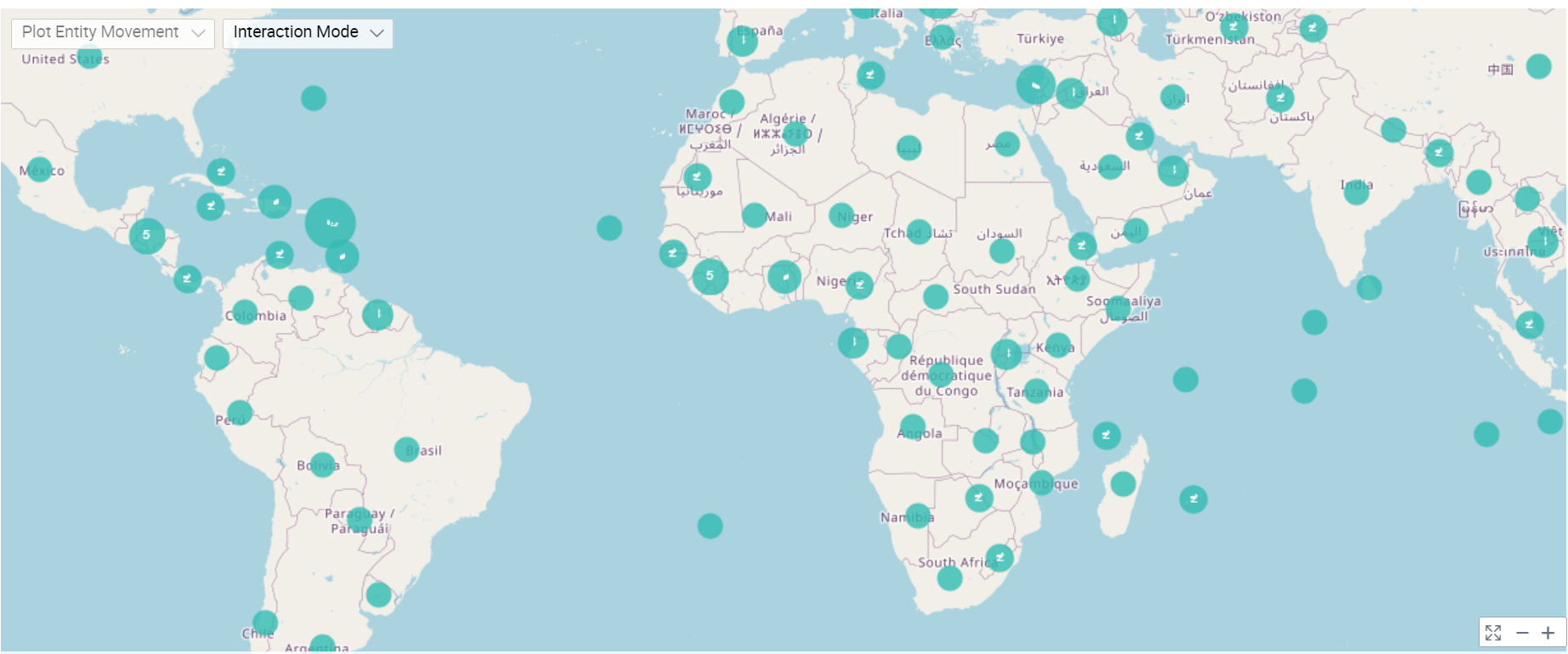
Configure GIS
- Select your GIS and open the Visualizations Panel.
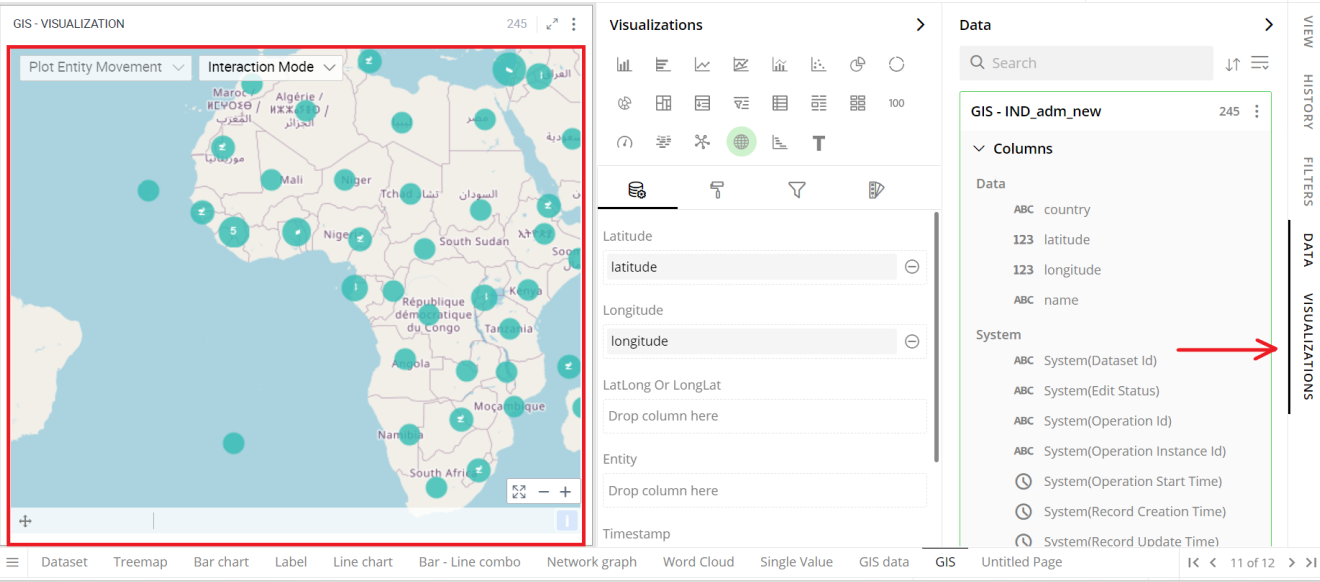
The following configuration options are available for GIS: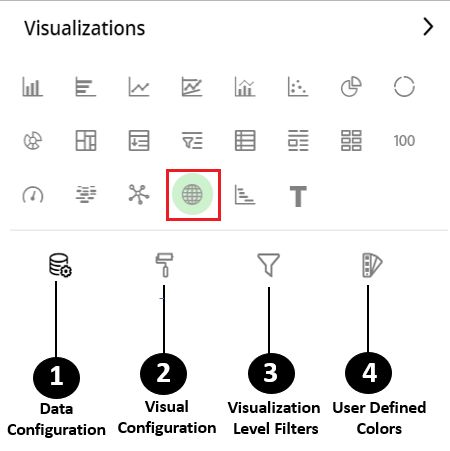
Data Configuration
 : It lets you choose columns for the following settings:
: It lets you choose columns for the following settings:View Configuration
 : It lets you configure the visual appearances and interactions of the GIS.
: It lets you configure the visual appearances and interactions of the GIS.Visualization Level Filters
 : It lets you filter the data in the specific visualization without impacting other visualizations.
: It lets you filter the data in the specific visualization without impacting other visualizations.
Refer here to learn more about Visualization Level Filters.
User-Defined Colors
 : It lets you add meaning to a data point by associating a specific color to it or differentiate a data point from the rest.
: It lets you add meaning to a data point by associating a specific color to it or differentiate a data point from the rest.
Data Configuration
- Click
 icon for data configuration options.
icon for data configuration options.
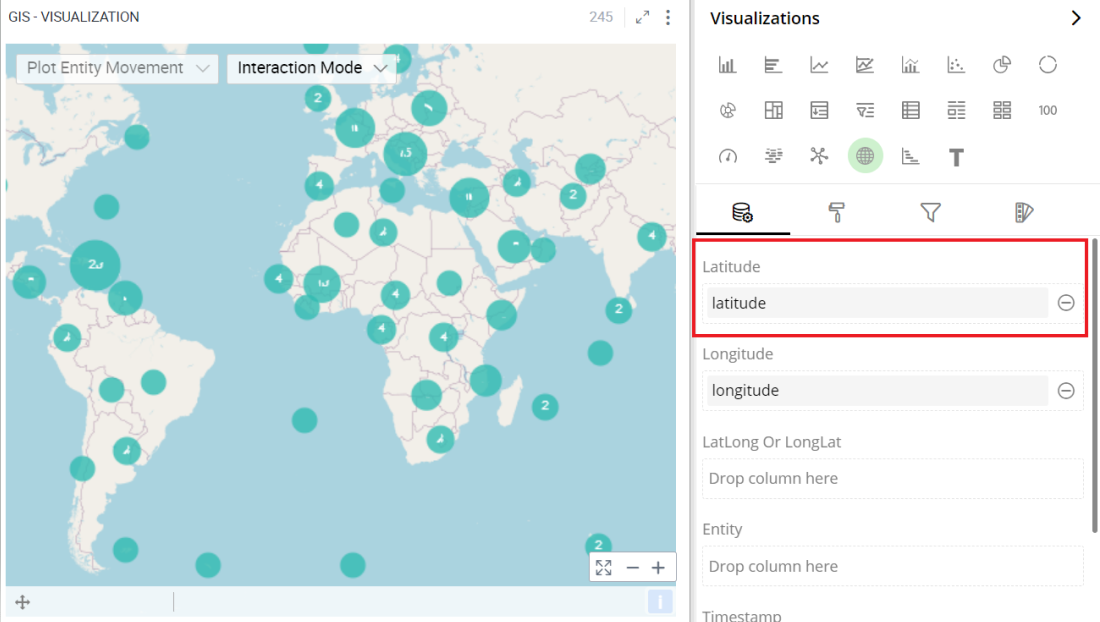
Latitude
You can specify the column to be displayed as Latitude in GIS.
To change the column:
Click on the
 icon to remove the existing column.
icon to remove the existing column.Drag the desired column from the Data Panel and drop it onto the Visualizations Panel’s “Latitude” section.
Note: You can also type the column name in the Data Panel to quickly find it.
Longitude
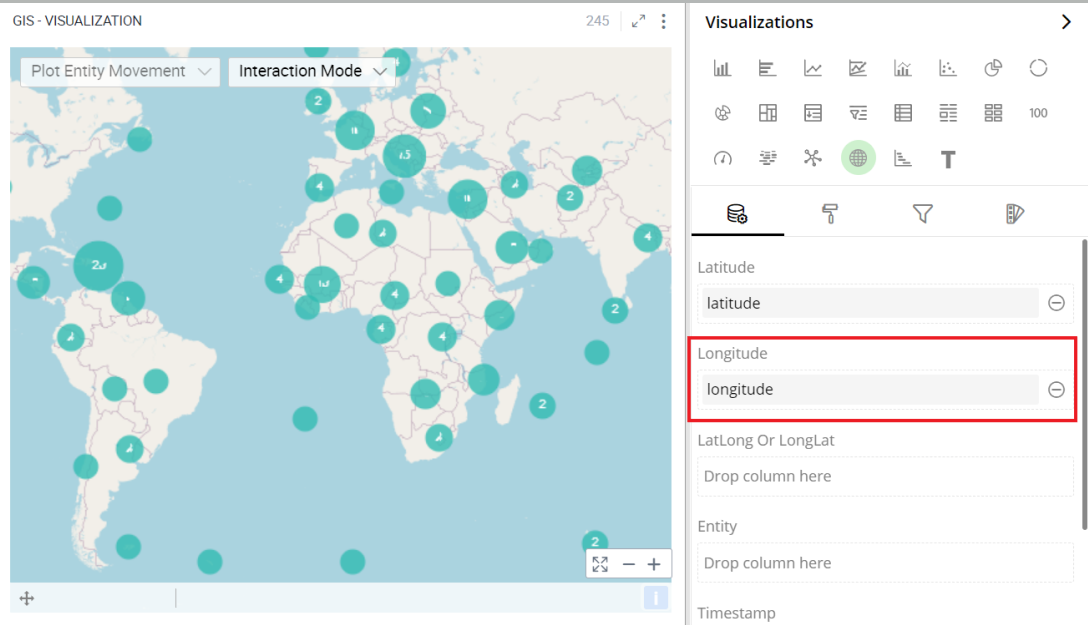
Here, you can specify the column to be displayed as Longitude in GIS.
To change the column:
Click on the
 icon to remove the existing column.
icon to remove the existing column.Drag the desired column from the Data Panel and drop it onto the Visualizations Panel’s “Longitude” section.
Note: You can also type the column name in the Data Panel to quickly find it.
LatLong Or LangLat
Here you can provide column where it contains geographic coordinates in the form of latitude and longitude. You drag and drop the column from your dataset in LatLong or LongLat data configuration.
Latitude, Longitude and Latlong or Longlat support for Multivalued Fields in GIS
Gathr Analytics supports multi-value inputs for latitude, Longitude and Latlong or Longlat fields allowing you to input multiple geographic coordinates from your data set.
| Entity | Latitude | Longitude | Latlong | Longlat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle A | 34.05, 36.60, 38.07 | 77.20, 72.87, 80.35 | 28.61,77.20, 19.07, 72.87, 12.97, 77.59 | 77.20, 28.61, 72.87, 19.07, 77.59, 12.97 |
| Vehicle B | [40.08, 45.45] | [77.50, 75.60] | [13.08, 80.27, 22.57, 88.36] | [80.27, 13.08] |
These formats represented in the illustration shows multi value support for multiple sets of coordinates.
Entity
It denotes individual geographic entities such as points, lines, or polygons. You can drag and drop appropriate column from your dataset.
Entity Movement
Entity movement refers to the dynamic tracking and visualization of the paths or trajectories of geographical entites (such as vehicles, animals, or weather systems) over time, illustrating their changes in location on the map.
- Data Configuration
To plot the entity movement, input Latitude, Logitude, Entity and Timestamp fields in data configuration tab, ensuring with relevant columns present in your data.
- Visual Configuration
In Visual Configuration tab, you can configure Entity Movement by enabling the legend with the toggle switch. To provide view controls to the app user toggle on the settings for entity movement and entity legend.
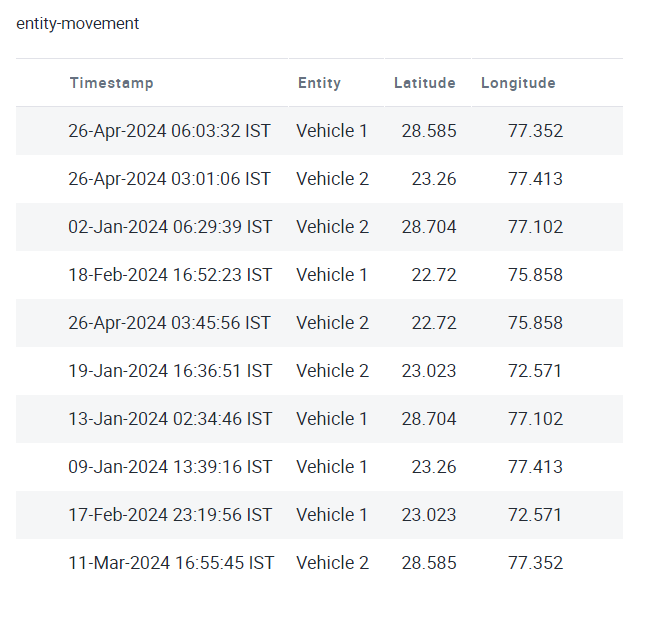
Let’s understand entity movement with the following illustration:
We have sample data containing location information for two vehicles (Vehicle1 & Vehicle 2) between January 1st, 2024 and April 30, 2024.
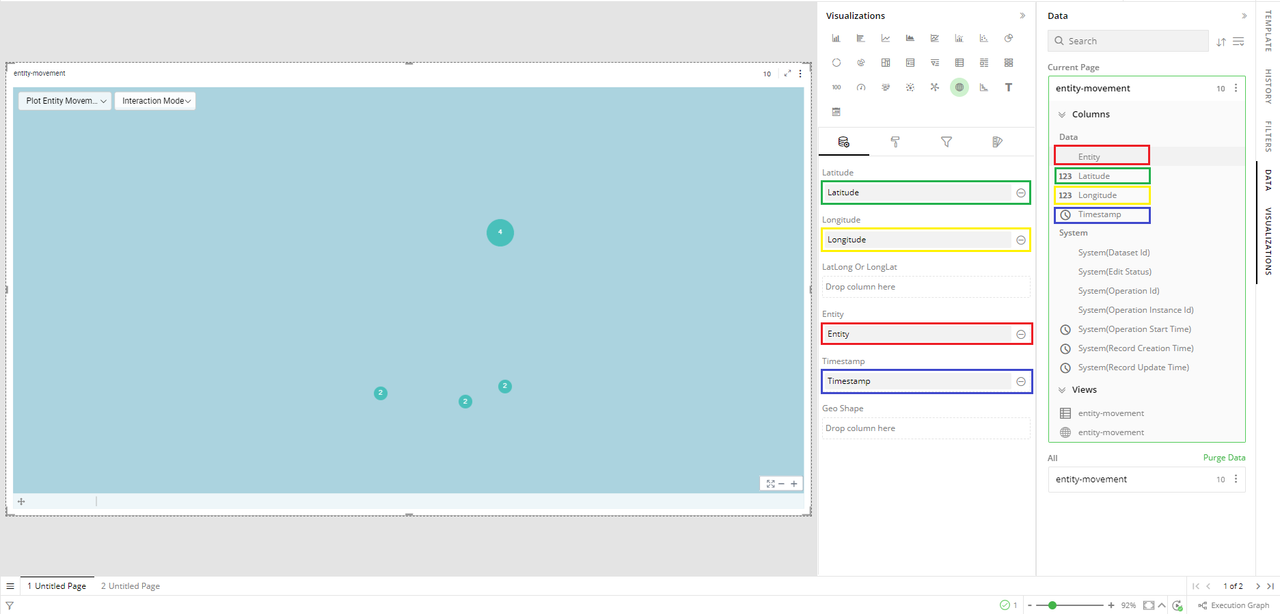
To plot entity movement visualizations for Vehicle 1 and Vehicle 2, drag and drop relavant columns available in your data to the latitude, longitude, entity and timestamp columns available in Data Configuration tab as shown in the image below.
Additionally, there is a short video created to show entity movement.
Timestamp
It defines the geometric shape of geographic features, such as polygons for areas or lines for routes.
Visual Configuration
- Click the
 icon for visual configuration settings.
icon for visual configuration settings.
GIS Settings
GIS settings allows users to configure features such as Heat Maps, Markers, Labels to customize visual representations of geagraphical data on maps.
To configure, click on GIS Setting to expand configuration options.
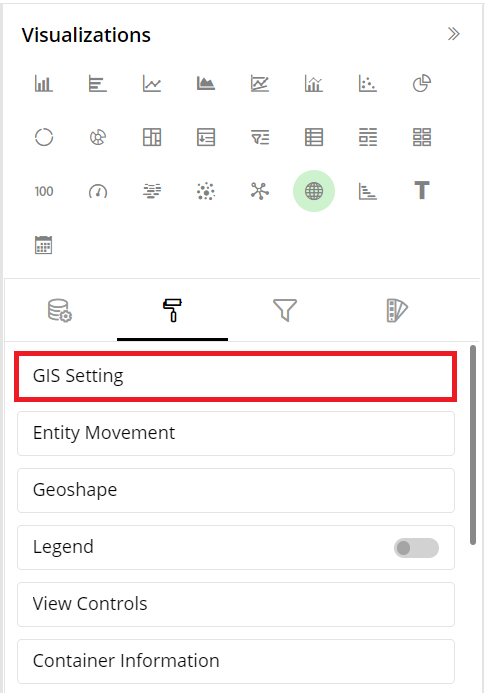
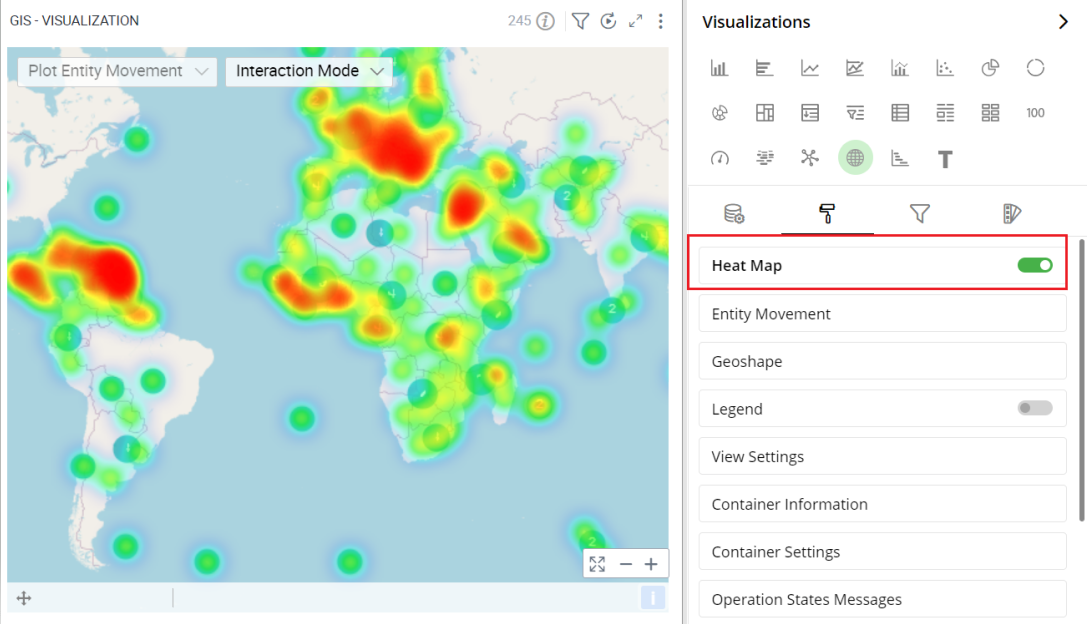
Heat Map lets you customize the representation of data in which values are represented by colors.
To turn Heat Map on or off, select the toggle switch next to Heat Map.
Marker settings toggles the display of specific points or locations on the map.
To turn Marker on or off, select the toggle switch next to Marker.
Label setting toggles the visibility of text labels associated with map features of data points.
To turn Label on or off, select the toggle switch next to Label.
View Controls
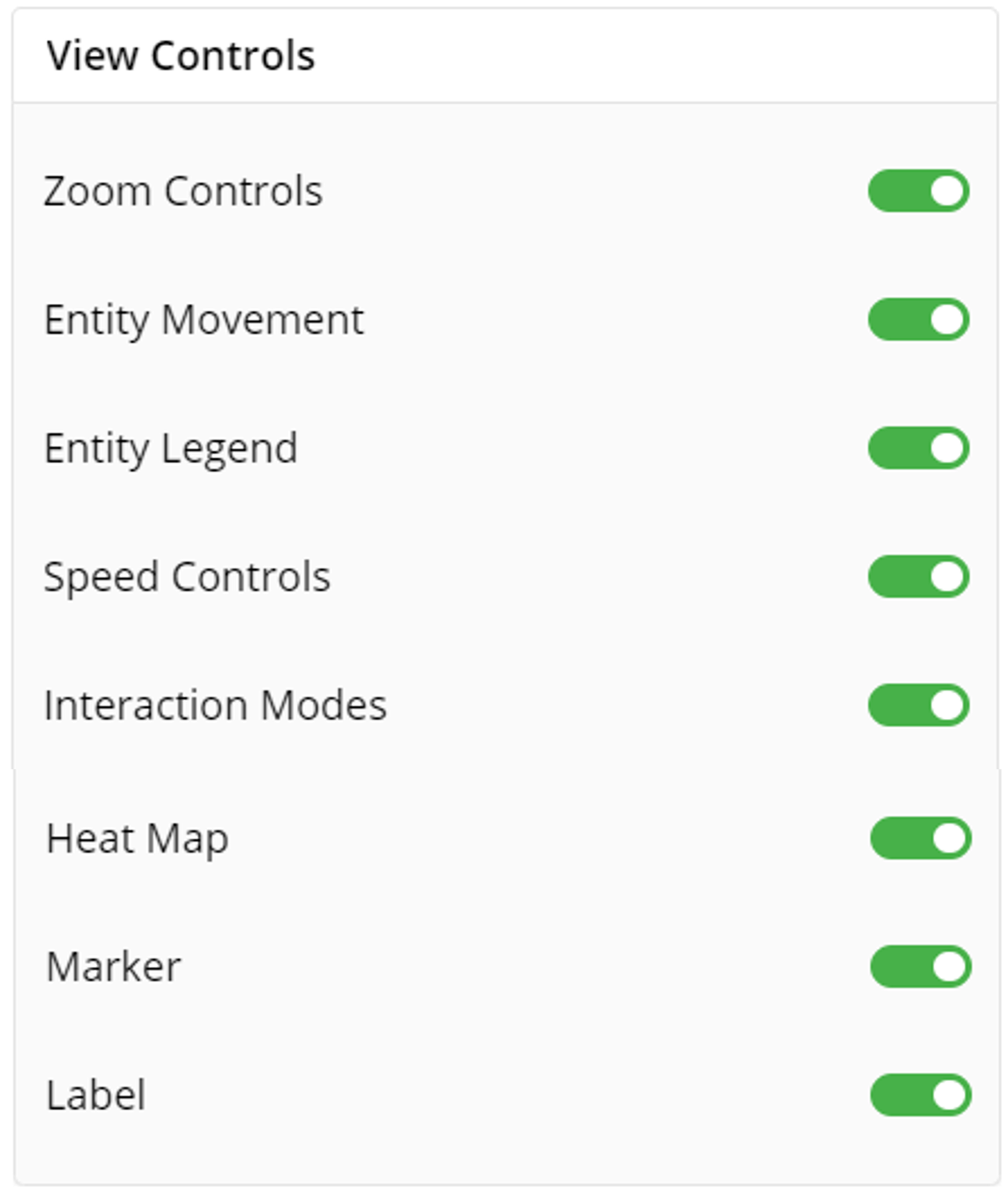
View control settings allows users to manage various controls such as zoom, entity movement, entity legend, etc. for better navigation and interaction with visualizations.
To configure, click on View Controls to expand configuration options.
You can toggle Zoom Controls, Entity Movements, Entity Legends, Speed Controls, Interaction Modes, Heat Map, Marker and Label to allow user to configure geographical visualizations available.
Heat Map
Heat Map lets you customize the representation of data in which values are represented by colors.
- To turn Heat Map on or off, select the toggle switch next to Heat Map.
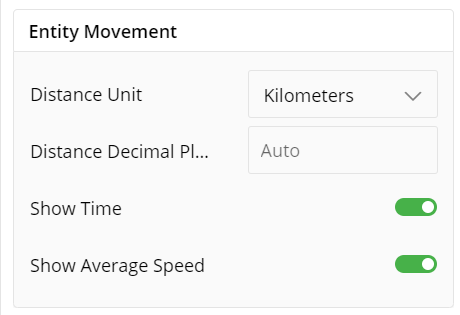
Entity Movement
Entity Movement stimulates movement of individual entities on a map. We can denote an movement of an entity from Distance Unit, Distance Decimal Places, toggle to Show Time and Show Average Speed.
Geoshape
Under Geoshape visual configuration you have following settings:
- Distance Unit: It specifies the unit of measurement for distances within the geoshape, such as kilometers, meters, or miles.
- Distance Decimal Places: It determines the number of decimal places displayed in distance measurements, offering precision control.
- Coordinate Precision: It sets the level of detail for coordinates defining the geoshape, affecting accuracy and rendering smoothness.
- Radius Limit: It establishes a maximum allowable radius for circular geoshapes, limiting their size within the visualization.
- Length limit: It defines the maximum permissible length for line-shaped geoshapes, restricting their extent in the visualization.
- Breadth limit: It specifies the maximum width for polygon geoshapes, constraining their breadth within the visualization.
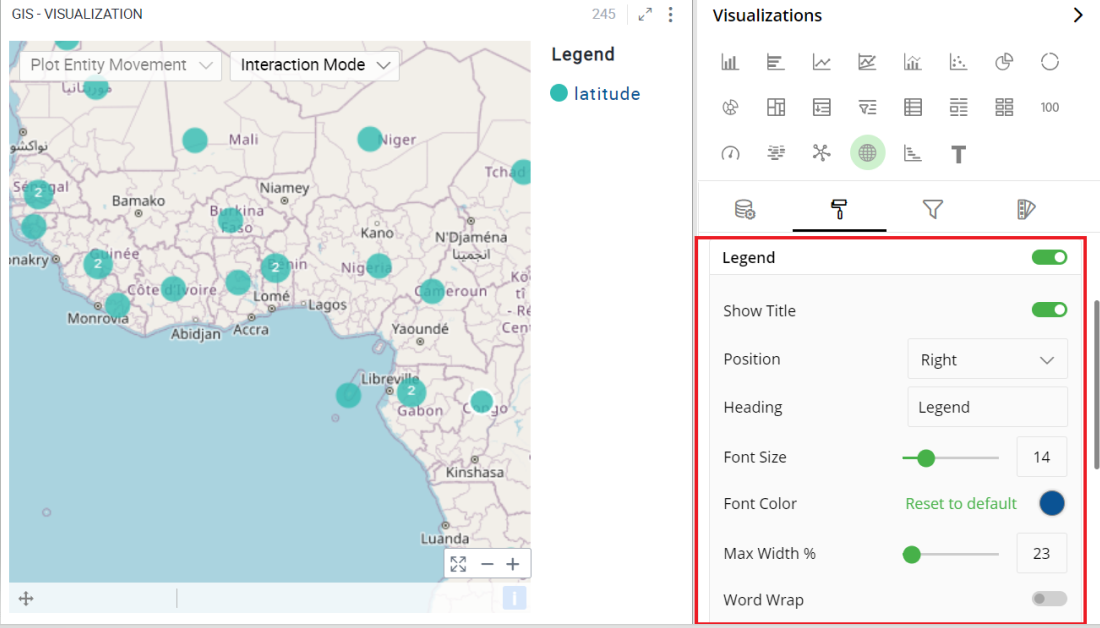
Legend
Legend helps you identify and correlate data on your chart. They provide an overview of the different data points on the chart along with the associated colors.
To turn legends on or off, select the toggle switch next to Legend.
To show title, select the toggle switch next to Show Title.
Select legend position (Left, Right).
Select legend position for vertical alignment (Top, Bottom, Center).
Enter the text to change the legend heading.
Move the slider or provide the value for font size and Max Width in %.
Click on the color and select a Font color from the color grid. To restore the default color setting, click ‘Reset to Default’.
To turn Word Wrap on or off, select the toggle switch.
Note: Click on legend items and related data will be highlighted in the visualization.
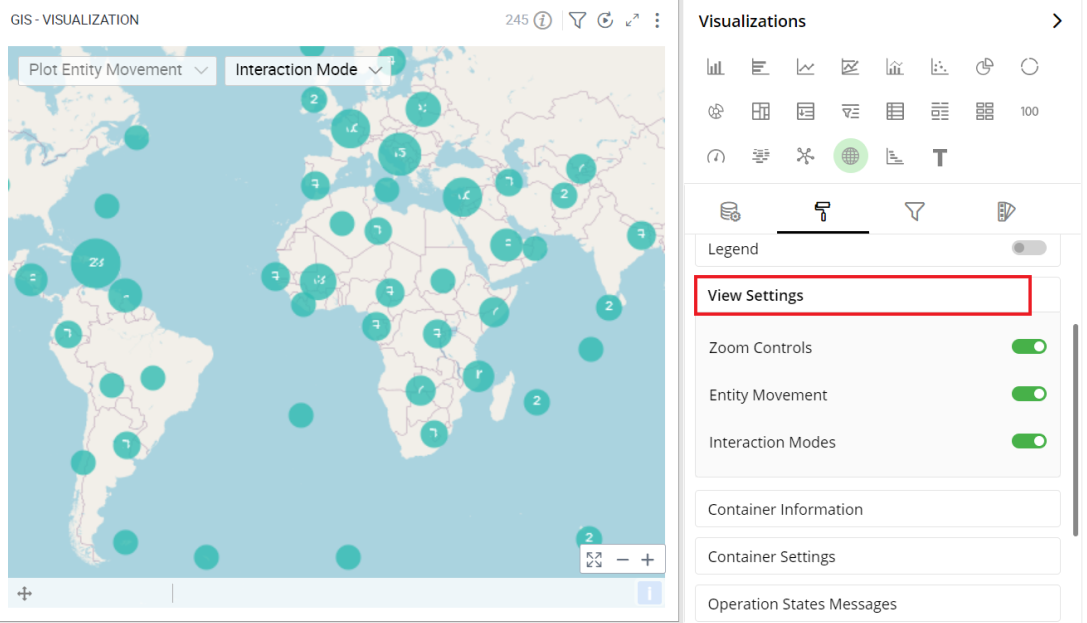
View Settings
View Settings helps you view and explore the data on your GIS chart. To turn the Zoom Controls, Entity Movements, and Interaction Modes on of off, select the toggle switch.
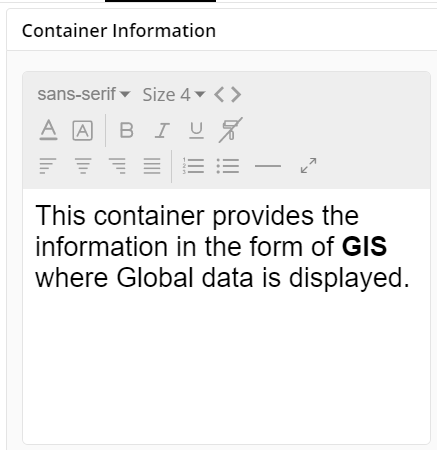
Container Information
- You can enter the details of a container in the Container information and change its Font, Size, Color, etc.
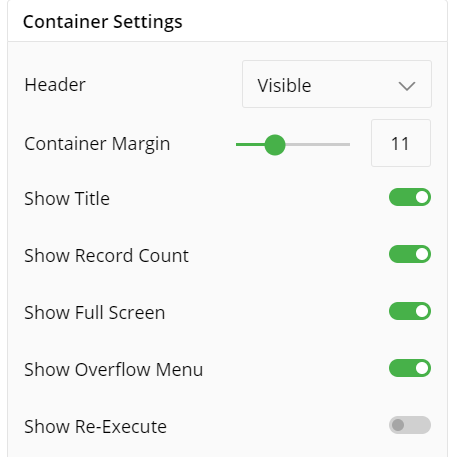
Container Settings
- Change the container Settings for the following fields such as Header, Container Margin, Container Margin, etc. as per your requirements.
The following figure displays the effect of various settings for GIS.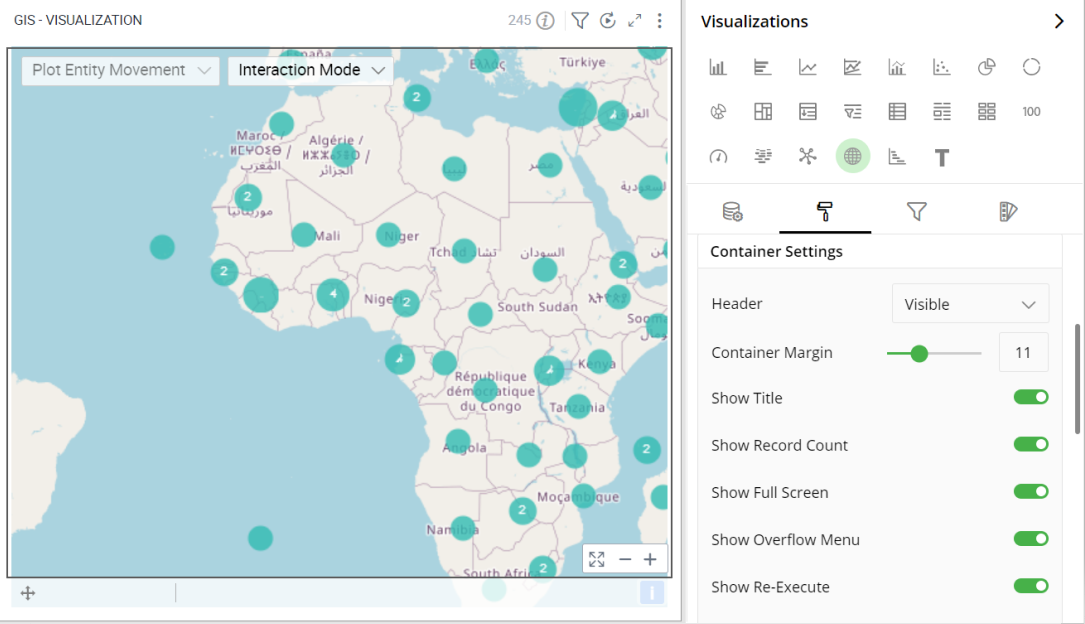
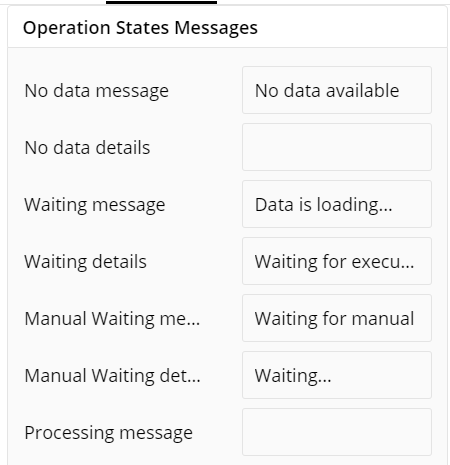
Operation States Messages
- Add/edit the Operation States Messages such as Waiting message, Waiting details, Processing message, etc. to provide a concise information about operation states.
Formulae States Messages
Add/edit the States Messages such as Waiting message, Waiting details, Processing message, etc. to provide a concise information about Formulae states.
Refresh Rate
- Change the Refresh Rate such as Low, Medium, High resolution to display updates in your application.
Visual Interactions
- Select the target behavior and coordinated visualization scope from the settings, as shown below:
To learn more, refer to section- ‘Configure Coordinated Visualization’.
User-Defined Colors
- Click on the
 icon for user-defined color settings.
icon for user-defined color settings.
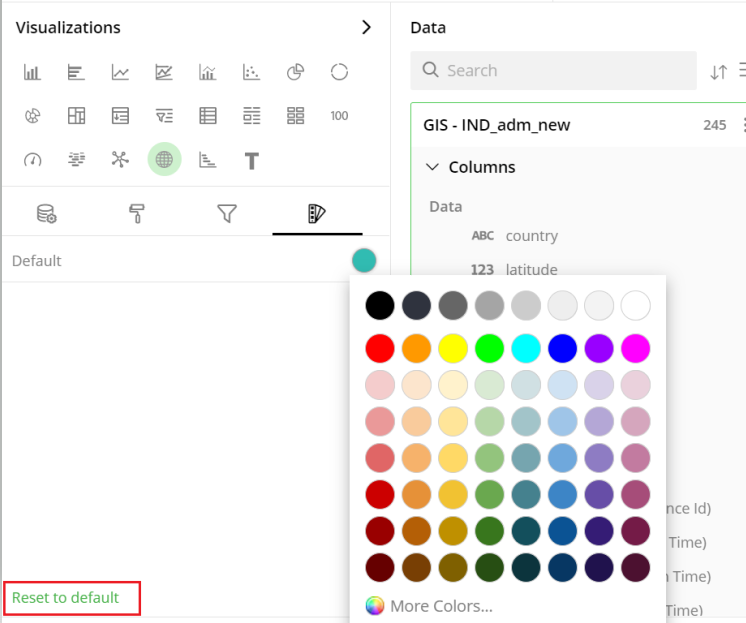
Colors for Individual Data Item
It lets you add meaning to a data item by associating a specific color to it and differentiate some data items from the rest.
For example, the red and green color may be used to represent “Off Track” and “On Track” issues, respectively. Whereas, orange color may be used for the “Bugs” type of issues to draw attention.
To change the colors:
Click on the color picker next to the data item for which you want to change the color.
Select the color from the available color grid or click ‘More Colors’.
To restore default settings, click on ‘Reset to default’.
Configuration Options in Full-Screen Mode
Visualization can be seen in full-screen mode by clicking on the  icon.
icon.
Note: Visualizations Panel is not accessible in full-screen mode.
- Click on the
 icon at the top-right corner of the container.
icon at the top-right corner of the container.
Select ‘Configure View’ the overflow menu.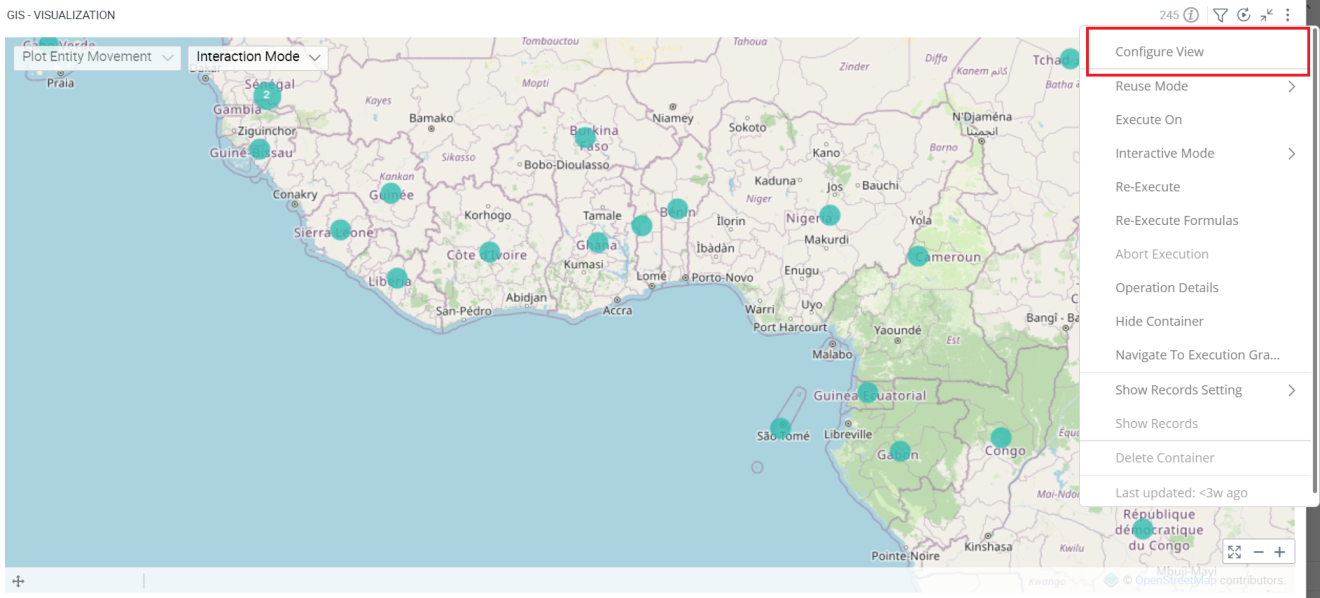
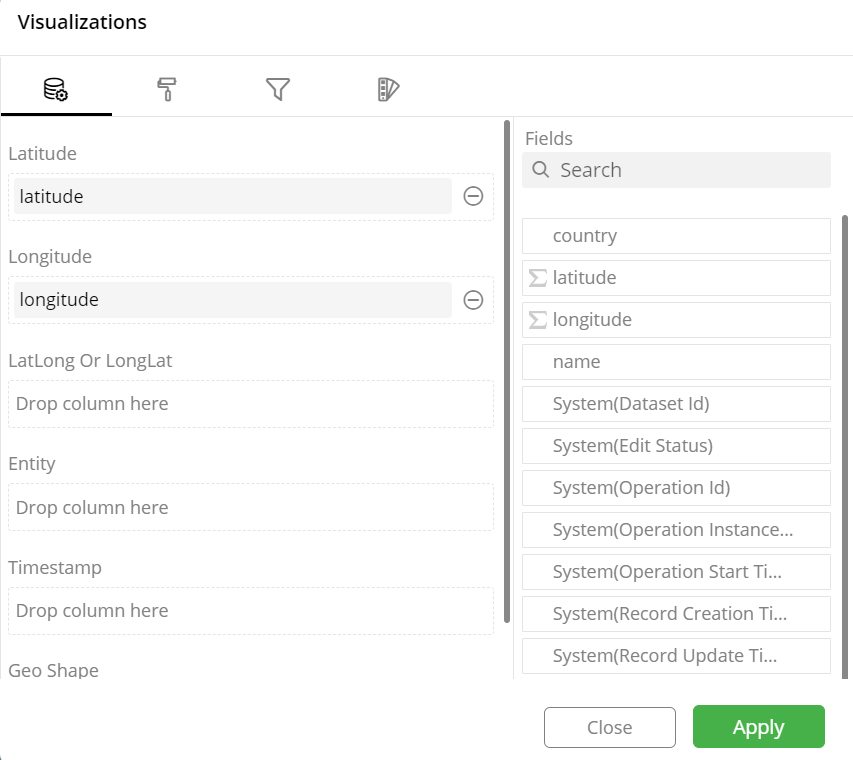
A pop-up form with all the relevant configuration options will appear on the screen.
Configure your Visualizations and click on ‘Apply’.
If you have any feedback on Gathr documentation, please email us!