JDBC ETL Target
In this article
JDBC Emitter allows you to push data to relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle DB, and MS-SQL.
JDBC emitter also enables you to configure data on DB2 database using JDBC emitter for both batch and stream.
It is enriched with lookup functionality for the DB2 database so that you can enrich fields with external data read from DB2. Select a DB2 connection while configuring JDBC emitter.
Target Configuration
Fetch From Target/Upload Schema File
The data source records needs to be emitted to a JDBC Database target table.
In case if the Gathr application has access to a target table in the JDBC Database, choose the option Fetch From Target.
In case if Gathr application does not have access to a JDBC Database target table, you can choose the option Upload Schema File in order to map the JDBC Database table columns with the source columns during design-time and confirm the data type for each column. In such cases you can run the application in a registered environment, that has access to all the required resources. During run-time, the application will run on the registered cluster of your choice picking up the configuration values as provided during application design.
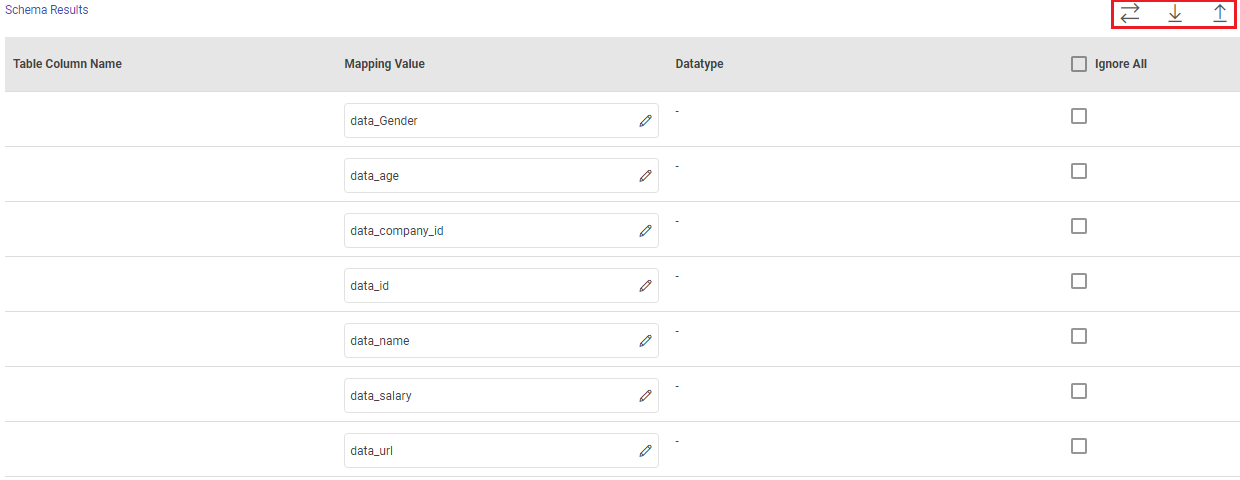
When you select the Upload Schema File option, a Schema Results section will get displayed at the bottom of the configuration page.
You can then download the sample schema, provide JDBC Database - Table Column Name against mapping values and verify the data type.
Once it is updated, you can upload the saved file to see a sample of how the records from a source column will be written into the corresponding mapped JDBC Database column.
Save as Data Asset: Select checkbox to save the schema as a data asset in Gathr.
Data Asset Name: Provide a name for the data asset to be saved.
Connection Name: Connections are the service identifiers. A connection name can be selected from the list if you have created and saved any JDBC connection details earlier. Or create one as explained in the topic - JDBC Connection →
Schema Name: Existing database Schema Names whose tables are fetched. (for MSSQL, DB2 and POSTGRES)
Table Name: Existing table name of the specified database.
Enable Batch: Enable parameter to batch multiple messages and improve write performances.
Batch Size: Batch Size, which determines how many rows to insert per round trip. This can help the performance on JDBC drivers. This option applies only to writing. It defaults to 1000.
Save Mode: Save Mode is used to specify the expected behavior of saving data to a data sink.
Ignore Error Check this option to ignore the ingestion errors. For.ex., duplicate key constraint.
Priority Priority defines the execution order for the emitters.
Append: When persisting data, if data/table already exists, contents of the Schema are expected to be appended to existing data.
Overwrite: When persisting data, if data/table already exists, existing data is expected to be overwritten by the contents of the Data.
Upsert: When persisting data, if the data already exists, the operation combines existing data with the new data, updating records when there are conflicts and adding new records when necessary. This mode is suitable for merging data and ensuring data consistency by applying a combination of inserts and updates as needed.
Update: The existing data in the designated target table will be updated, and any new data will be inserted.
Enable Trigger: Trigger defines how frequently a streaming query should be executed.
Processing Time: It will appear only when Enable Trigger checkbox is selected.
Processing Time is the trigger time interval in minutes or seconds.
Create Table: This field gets displayed if Upload Schema File option is used to provide column mapping. Check this field if you want to create a new table in the JDBC database. If unchecked, ensure the provided table name matches an existing table in the database.
Create Table Query: Enter the SQL query for creating the table. This is required if the Create Table option is checked.
An example showing the length of the Varchar2 datatype:
CREATE TABLE example_table (column1_name VARCHAR2(50),column2_name numeric,column3_name timestamp)
In this example, column1_name is defined with a Varchar2 datatype with a length of 50 characters. Adjust the length as needed for your specific requirements.
Add Configuration: Enables to configure custom properties.
Example: key=createTableOptions value=ENGINE=Log()
The value for this configuration property will depend upon the type of JDBC database target that you have connected.
If you are connected to the Clickhouse DB and want to create a new table or if the save mode is set to Overwrite, then the configuration property can be given as follows:
key=createTableOptions value=ENGINE=Log()
Schema Results: Map the values coming in pipeline with any table columns name.
Table Column Name: The columns from the selected table are populated here.
Mapping Value: Enter a mapping value to the corresponding column.
Datatype: The data type of the value, i.e., String, Int, Text and so on.
Ignore All: Use Ignore All or selected fields while pushing data to emitter.
Post Action
To understand how to provide SQL queries or Stored Procedures that will be executed during pipeline run, see Post-Actions →
Notes
Optionally, enter notes in the Notes → tab and save the configuration.
If you have any feedback on Gathr documentation, please email us!