The objective of this topic is to assist the user to install Gathr on an Azure environment.
Hardware and Software Configurations
Create Azure VM, preferably on the same VNET and Subnet where the Azure Databricks cluster is running with the below minimal specification.
Prerequisites | Details |
|---|---|
Machine Type | Standard D8s v3 (8 vcpus, 32 GiB memory) |
Disk Space | 100 GB (Min) |
Operating System | Linux (Centos 7.9.2009) |
sudo Access | Required during installation. |
Internet Access | Optional [preferred during the installation. Otherwise, the required software packages and their dependency should be available on Azure VM]. |
Open the below ports in VM’s NSG:
Serial No | Service | Source | Destination | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Zookeeper | CIDR range of Databricks Cluster | Azure VM | 2181 |
2 | Gathr (Non-SSL/SSL) | CIDR range of User | Azure VM | 8090/8443 |
3 | RabbitMQ (Non-SSL/SSL) | CIDR range of User | Azure VM | 5672,15672/15671 |
4 | Elasticsearch | CIDR range of User | Azure VM | 9200-9300 |
5 | PostgreSQL | CIDR range of User | Azure VM | 5432 |
Note:
CIDR range of user: This means that the customer needs to whitelist the IP ranges where the user is trying to access the Web UI of Gathr, RabbitMQ, and Elasticsearch.
CIDR range of Databricks Cluster: This means the customer needs to whitelist the IP ranges of the Databricks cluster on Azure VM.
Azure Portal Access
A virtual machine with the following resources should be available to setup Gathr:
- Resource Group
- Virtual machines
- Virtual Networks
- Subnet
- Network Security Group
- Azure Databricks
Below details are required to configure Azure Databricks with Gathr
- Azure Databricks instance URL
- Azure Databricks Authentication token
- Azure Databricks DBFS Path
Gathr Installation specific prerequisites
- The SSH access should be available for Azure VM to Setup Gathr.
- The Linux SSH user used for Gathr installation should have the sudo privilege.
- Make sure the Gathr_Setup_bundle (tar.gz) and other artifacts should be downloaded from centralized location provided by the Gathr Support team and make it available on Azure VM.
- Valid Gathr license file should be available during the installation (provided by the Gathr Support team).
- Ensure the connectivity between Gathr VM, Azure Databricks cluster, and any external components (Hadoop, Kafka, Solr, etc.) if required.
The below specified software should be installed on Azure VM as part of the Gathr installation.
Prerequisites | Details |
|---|---|
JAVA Open JDK | 1.8.0 |
Gathr [Cloud Build] | 4.9.0 |
RabbitMQ | 3.8.17 |
Elasticsearch | 6.4.1 |
Zookeeper | 3.5.7 |
PostgreSQL | 10 |
RabbitMQ, Elasticsearch components are optional; however, pipeline monitoring and error handling features won’t be provided in Gathr if these are not available.
Note: The Hadoop components (Kafka, HBase, Hive, etc.) are optional and can be installed and configured with Gathr depending upon the use case requirements.
To setup Gathr, you should have sufficient privileges to create and manage the resources (Resource Group, Virtual machines, Virtual Networks, Subnet, Network Security Group, Azure Databricks) in Azure.
Note: Hadoop components are optional; depending upon the requirements. You may need to install the Hadoop services (HDFS, Hive, Yarn, etc.) manually and update the configurations accordingly in Gathr.
Create Virtual Machine
Hardware/Software | Requirement |
|---|---|
Machine Type | Standard D8s v3 (8 vcpus, 32 GiB memory) |
Disk Space | 30 GB |
Operating System | Linux (Centos 7.9.2009) |
sudo Access | Required during installation |
Internet Access | Optional [preferred during the installation] |
- Type virtual machines in the search.
- Under Services, select Virtual machines.
- Select Create and then click Virtual machine on the Virtual machines page. The Create a virtual machine page opens.
- In the Basics tab, under Project details, make sure that the correct subscription is selected and then create a new resource group. Type myResourceGroup for the name.*.
- Under Instance details, type tomcatVM for the Virtual machine name, and choose CentOS Gen1 for your Image. Leave the other defaults. The default size and pricing are only shown as an example. Size availability and pricing are dependent on your region and subscription.
- Under Administrator account, select Password.
- Under Inbound port rules > Public inbound ports, choose to Allow selected ports and then select SSH (22) and HTTP (80) from the drop-down.
- Leave the remaining defaults and then select the Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- On the Create a virtual machine page, you can see the details about the VM you are about to create. When you are ready, select Create.
- When the deployment is finished, select Go to resource.
- On the page for your new VM, select the public IP address and copy it to your clipboard.
Below are the ports that need to be opened in VM Security Group
Serial No | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|
1 | Zookeeper | 2181 |
2 | Gathr (Non-SSL/SSL) | 8090/8443 |
3 | RabbitMQ (Non-SSL/SSL) | 5672,15672/15671 |
4 | Elasticsearch | 9200-9300 |
5 | PostgreSQL | 5432 |
This section describes the steps required to install the prerequisite software on Virtual Machine launched on Cloud.
ssh into the Gathr VM to continue with the following steps
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.312.b07-1.el7_9.x86_64 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH |
Set java home in. bashrc
This is an optional component. However, it is important as it is used for pipeline error handling in Gathr.
Install this package before installing RMQ:
yum -y install epel-release yum -y install erlang socat |
Download the package
Start using this command:
systemctl start rabbitmq-server |
Enable it with this command:
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server |
To check the status, use this command:
systemctl status rabbitmq-server |
Enable the plugins with this command:
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management |
To create a test user:
rabbitmqctl add_user test test rabbitmqctl set_user_tags test administrator rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / test ".*" ".*" ".*" |
Install Zookeeper 3.5.7 as follows:
Copy the zookeeper tar file either from sax_bundle.
Extract it:
tar –zxvf apache-zookeeper-3.5.7-bin.tar.gz Open /zookeeper-3.5.7/conf and edit zoo.cfg. |
Set the IP and Port in
zoo.cfg file: server.1=IP:2888:3888
Start the zookeeper
/zookeeper-3.5.7/bin with ./zkServer.sh start.
Install Postgres 10 as follows:
1. Install Postgres repo as a root user into the system:
2. Install Postgresql10:
yum install postgresql10-server postgresql10 |
3. Initialize PGDATA:
/usr/pgsql-10/bin/postgresql-10-setup initdb Start the Postgres: systemctl start postgresql-10.service |
4. Login into Postgres: su - postgres -c "psql"
5. Change the Postgres password
postgres=#\password postgres
Settings for PostgreSQL
Login as a Postgres user: su – postgres.
cd /10/data and edit the pg_hba.conf. |
Add the IPs in IP4 to allow the permission:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 host replication postgres 10.1.2.0/24 md5 |
Edit the postgresql.conf and replace listen_address from localhost to *
.
listen_addresses = '*' |
Restart the postgres: systemctl restart postgresql-10.service
This is an optional component; however, it is important as it will be used for monitoring Gathr pipelines.
Install Elasticsearch 6.4.1 as follows
- Copy Elasticsearch from sax_bundle.
- Extract the bundle.
- Open /elasticsearch-6.4.1/conf/elasticsearch.yaml and make these changes:
cluster.name: ES641 node.name: IP of the machine path.data: /tmp/data path.logs: /tmp/logs network.host: IP of the machine http.port: 9200 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["IP"] |
Setting for Elasticsearch
1. max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least [65536]
2. max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
For 1. Add this line in /etc/security/limits.conf
Note: Sax is the user from which you are starting elasticsearch.
sax soft nofile 65536 sax hard nofile 65536 sax memlock unlimited |
For 2. Run this command: sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
Start Elasticsearch in the background: nohup ./elasticsearch &
Install and run in embedded mode. Copy the Gathr tar file to the Virtual Machine. Extract the tar.
Run this command to start StreamAnalytix in embedded mode:
cd bin ./startServicesServer.sh -deployment.mode=embedded |
Note: Logs are located in <GathrInstallationDir>/logs and <GathrInstallationDir>/server/tomcat/logs directories.
You can check the log files in these directories for any issues during the installation process.
To open Gathr use the below command:
_IP>:8090/Gathr
Accept the End User License Agreement and hit the Next button.
The Upload License page opens.
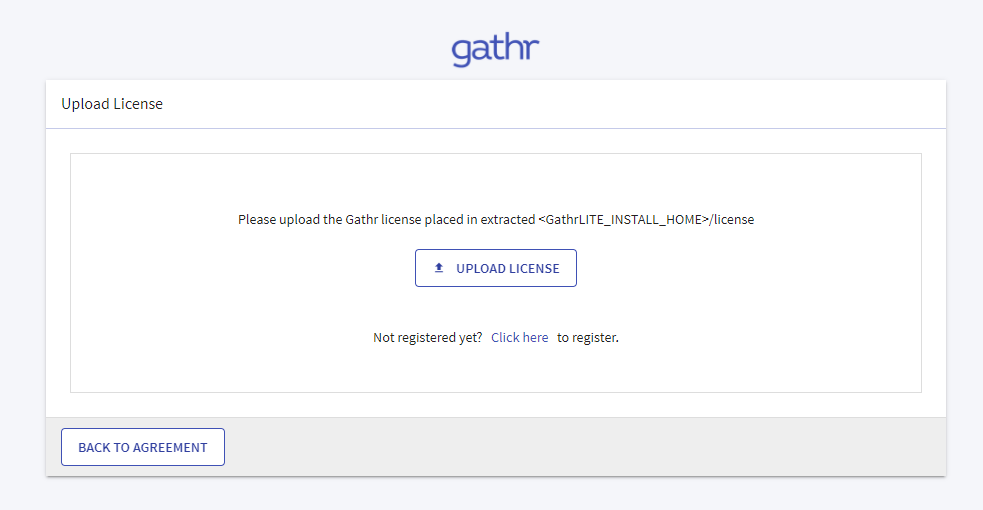
Upload the license and confirm.
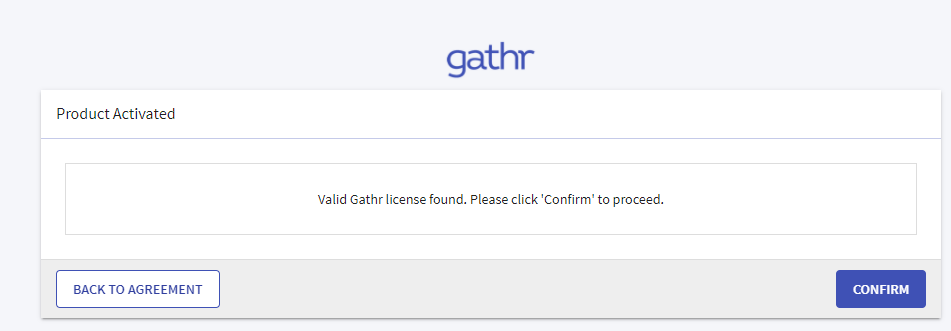
Login page is displayed.
Note: Now, the user will need to switch Gathr from embedded to cluster mode.
Follow the sections given below to switch Gathr from embedded to cluster mode:
Login to Gathr using the default username & password.
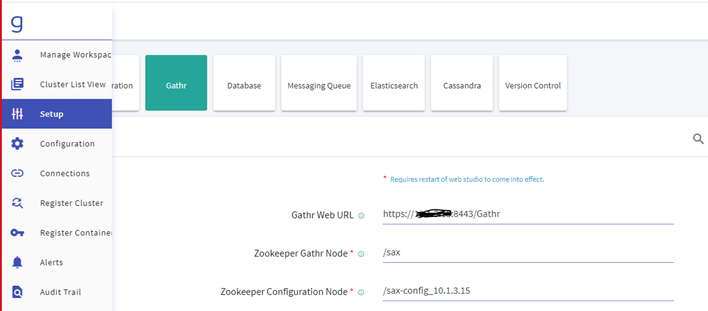
Navigate to the Setup >> Gathr and update the below details:
- Gathr Web URL
- Zookeeper Gathr Node
- Zookeeper Configuration Node
Navigate to the Setup >> Database and update the below details.
- Connection URL
- User
- Password
- Run Script
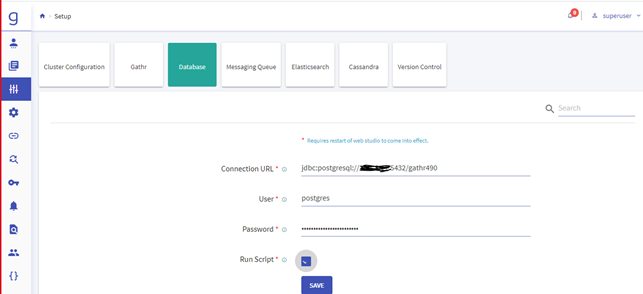
Note: Check the Run Script and click on Save. It will execute the DDL & DML in Gathr Metastore.
Navigate to the Setup >> Messaging Queue and update the below details:
- Messaging Type
- Host List
- User
- Password
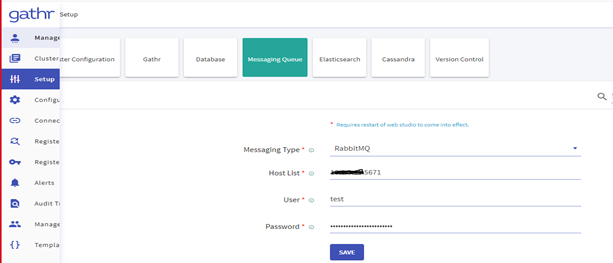
Navigate to the Setup >> Elasticsearch and update the below details:
- Elasticsearch Connection URL
- Elasticsearch Cluster Name
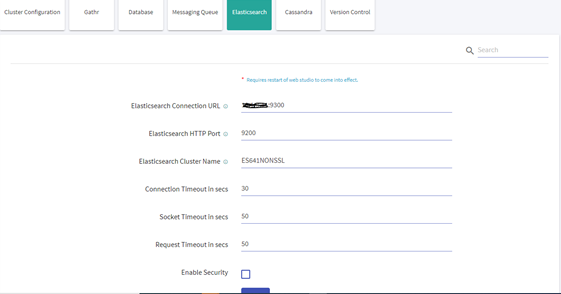
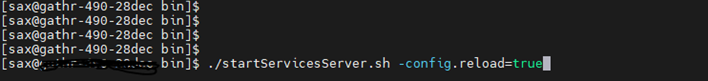
After updating the details, restart Gathr with -config.reload=true.
Copy Cloud Vendor-specific war
Copy Cloud Vendor-specific war file into tomcat
For Azure-Databricks:
cp <Gathrinstallationlocation>/lib/clusterMediator.war <Gathrinstallationlocation>/server/tomcat/webapps/ |
The war will get extracted in server/tomcat/webapps. Now stop tomcat and configure application files.
For Azure-Databricks:
cd <Gathrinstallationlocation>/bin ./stopServicesServer.sh update <Gathr installation location>/server/tomcat/webapps/cluster-mediator /WEB-INF/classes/application.properties file spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://<GathrPrivateIP>:5432/DBNAME |
Configure Cloud Vendor-specific details in YAML
Configure Databricks details in yaml
File: (<Gathrinstallationlocation>/Gathr /conf/yaml/env-config.yaml) databricks: dbfs.jar.uploadPath: "/sax-databricks-jars " mediator.address: "http://<GathrPrivateIP>:8090/cluster-mediator/" isEnabled: "true" authToken: "<authtoken>" instanceUrl: "https://<databricks-instance-url>" |
Copy jar & init-scripts on DBFS
curl 'https://<databricks-instance>/api/2.0/dbfs/put' -H "Authorization: Bearer <personal-access-token-value>" -F contents=@<Gathr installation location>/lib/spark-structured-sax-pipeline.jar -F path="<sax metadata on dbfs path>/spark-structured-sax-pipeline.jar" curl 'https://<databricks-instance>/api/2.0/dbfs/put' -H "Authorization: Bearer <personal-access-token-value>" -F contents=@$SAX_BUNDLE/init-scripts.sh -F path="<sax metadata on dbfs path>/init-scripts.sh" |
Restart in Cluster Mode and upload license
cd <Gathrinstallationlocation>/bin ./startServicesServer.sh –config.reload=true |
In case there are any updates to be done in configurations, you can restart Gathr by providing the below commands
./startServicesServer.sh -config.reload=true ./stopServicesServer.sh |
1. Stop/Kill the Bootstrap Process.
2. Delete Gathr installation directory and its dependencies (like RMQ, ZK etc)
3. Delete the Gathr database.